limits of hardness test to find material properties|hardness test depth : manufacturing The principle of electronically controlled and permanently monitored load application by means of a closed-loop control systemprovides decisive benefits for hardness testers.. The force is . Tuttnauer has been manufacturing sterilizers for over 95 years. As a global leader in .
{plog:ftitle_list}
View and Download Biobase BKQ-B Series maintenance manual online. Vertical Autoclave Sterilizer. BKQ-B Series laboratory equipment pdf manual download.
On the one hand, this test method can be used to find qualitative relations to other material properties (e.g., strength, stiffness, density) or to the material behavior under certain stresses (e.g., abrasion resistance).The principle of electronically controlled and permanently monitored load application by means of a closed-loop control systemprovides decisive benefits for hardness testers.. The force is .Properties include elastic modulus, ductility, hardness, and various measures of strength. .On the one hand, this test method can be used to find qualitative relations to other material properties (e.g., strength, stiffness, density) or to the material behavior under certain stresses (e.g., abrasion resistance).
Properties include elastic modulus, ductility, hardness, and various measures of strength. Mechanical properties desirable to the designer, such as high strength, usually make manufacturing more difficult. Integration of design and manufacturing. Tension, Compression and .Published August 18, 2023. Updated September 24, 2024. Hardness is a material’s ability to resist deformation at its surface. A measurement is taken of the resulting indentation and converted to a hardness value relative to the hardness scale of the particular test.Hardness and Strength • Studies have shown that (in the same units) the hardness of a cold-worked metal is about three times its yield stress (YS), for annealed metals, it is about five times. • A relationship has been established between the ultimate tensile strength (UTS) and the Brinell hardness (HB) for steels. In SI units the .Brinell Hardness Test In this test, a relatively large steel ball, specifically 10 mm in diameter is used with a relatively large force. The force is usually obtained with either 3000 kg for relatively hard materials such as steels and cast irons or 500 kg for softens materials such as copper and aluminum alloys.
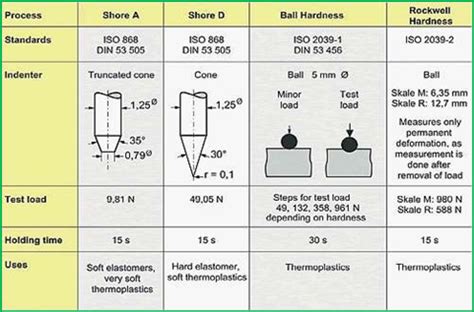
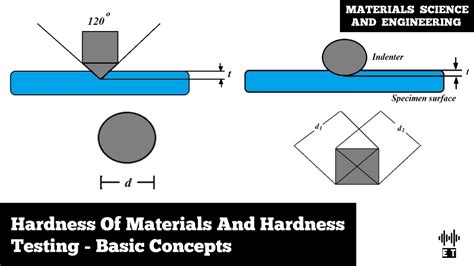
Hardness, a key property of materials, can be categorized into various types, each assessing different aspects of a material’s resistance to deformation. The three primary types are scratch, indentation, and rebound hardness, each providing unique insights into .material: from 1 (softest = talc) to 10 (hardest = diamond). Different types of quantitative hardness test have been designed (Rockwell, Brinell, Vickers, etc.). Usually a small indenter (sphere, cone, or pyramid) is forced into the surface of a material under conditions of .The extent of martensite formation in the steel at given distance from the quench, which can be determined by hardness testing in several areas of a sample, is what hardenability measures. Hardenability also determines the necessary cooling rate, fast or slow, for martensite formation.Hardness is the property of a material that enables it to resist plastic deformation, penetration, indentation, and scratching. Therefore, hardness is important from an engineering standpoint because resistance to wear by either friction or erosion by steam, oil, and water generally increases with hardness.
978-1-62708-346-1. Publication date: 2011. Hardness Testing: Principles and Applications is an in-depth study of one of the most fundamental properties of materials and the tools and techniques that have been developed to measure it.On the one hand, this test method can be used to find qualitative relations to other material properties (e.g., strength, stiffness, density) or to the material behavior under certain stresses (e.g., abrasion resistance).
Properties include elastic modulus, ductility, hardness, and various measures of strength. Mechanical properties desirable to the designer, such as high strength, usually make manufacturing more difficult. Integration of design and manufacturing. Tension, Compression and .Published August 18, 2023. Updated September 24, 2024. Hardness is a material’s ability to resist deformation at its surface. A measurement is taken of the resulting indentation and converted to a hardness value relative to the hardness scale of the particular test.Hardness and Strength • Studies have shown that (in the same units) the hardness of a cold-worked metal is about three times its yield stress (YS), for annealed metals, it is about five times. • A relationship has been established between the ultimate tensile strength (UTS) and the Brinell hardness (HB) for steels. In SI units the .Brinell Hardness Test In this test, a relatively large steel ball, specifically 10 mm in diameter is used with a relatively large force. The force is usually obtained with either 3000 kg for relatively hard materials such as steels and cast irons or 500 kg for softens materials such as copper and aluminum alloys.
Hardness, a key property of materials, can be categorized into various types, each assessing different aspects of a material’s resistance to deformation. The three primary types are scratch, indentation, and rebound hardness, each providing unique insights into .material: from 1 (softest = talc) to 10 (hardest = diamond). Different types of quantitative hardness test have been designed (Rockwell, Brinell, Vickers, etc.). Usually a small indenter (sphere, cone, or pyramid) is forced into the surface of a material under conditions of .The extent of martensite formation in the steel at given distance from the quench, which can be determined by hardness testing in several areas of a sample, is what hardenability measures. Hardenability also determines the necessary cooling rate, fast or slow, for martensite formation.
Hardness is the property of a material that enables it to resist plastic deformation, penetration, indentation, and scratching. Therefore, hardness is important from an engineering standpoint because resistance to wear by either friction or erosion by steam, oil, and water generally increases with hardness.
large autoclaves for sale
standards for hardness testing
standard hardness testing methods
how to measure hardness
Ensure hazard identification and risk assessment (model proforma) has been completed and documented in accordance with the OHS Regulations 2007. A copy of the hazard identification .Getting Started Before using the autoclave for the first time please take time to read the .
limits of hardness test to find material properties|hardness test depth